介绍
Frida是一款易用的跨平 Hook 工具, Java 层到 Native 层的 Hook 无所不能,是一种 动态 的插桩工具;
静态二进制插桩:在程序执行前插入额外的代码和数据,生成一个永久改变的可执行文件;
动态二进制插桩:在程序运行时实时地插入额外代码和数据,对可执行文件没有任何永久改变;
可以插入代码到原生 App 的内存空间中,动态的去监视和修改行为;
原生平台包括 Win、Mac、Linux、Android、iOS 全平台;
1、使用frida可以获取进程的信息(模块列表,线程列表,库导出函数);
2、可以拦截指定函数和调用指定函数,可以注入代码;
3、Frida的主要工作方式是将脚本注入到目标新的进程中,而且在执行过程中可以实时看到其中的变化;
原理
frida分为两部分,服务端运行在目标机上,通过注入进程的方式来实现劫持应用函数,另一部分运行在系统机器上
1、模拟器端/手机端安装一个frida-server程序
2、启动模拟器端/手机端的frida-server服务,然后把手机端的端口转发到PC端,
3、PC端编写python脚本进行通信,python脚本中需要hook的代码采用javascript语言。
frida主要用javascript来编写脚本,这是因为他会向被hook的目标进程中注入一个 JavaScript 引擎(如 QuickJS 或 V8),然后解释执行你写的js脚本,这里是解释执行而不是编译,JS 脚本不会被编译成 .so 或机器码,而是在运行时由嵌入的 JS 引擎逐行解释。所以 Frida 脚本是动态脚本,修改后无需重新注入。
frida具体hook流程为:劫持了程序的控制流,导向 Frida 编写的脚本
frida主要通过两种方式劫持控制流
-
Inline Hook(最常用):
-
在目标函数开头覆盖几条指令(如 x86-64 上写
jmp) -
跳转到 Frida 的 trampoline 代码
-
执行你的
onEnterJS 回调 -
恢复现场,继续原函数(或跳过)
-
PLT/GOT Hook(针对动态库调用)
-
修改 PLT(Procedure Linkage Table)中的跳转地址
-
适用于 hook
libc函数(如open,read)
包含的工具
frida-tools中包含各种工具
基础使用
c程序hook
安装可以参考官方文档,比较简单
pip install frida-tools这里写一个简单的验证密码的c程序来测试
#include <stdio.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
int verify_password(char* input) {
char secret[] = "supersecret123";
return strcmp(input, secret) == 0;
}
int main() {
char user_input[64];
// 为了打印出 verify_password 的地址
printf("verify_function is at %p", verify_password);
printf("Enter password: ");
fflush(stdout);
read(0, user_input, 63);
user_input[strcspn(user_input, "\n")] = 0;
if (verify_password(user_input)) {
printf("Access granted!\n");
// 模拟执行敏感操作
system("echo 'Running critical task...'");
} else {
printf("Access denied.\n");
}
return 0;
}这里我们加了一个打印函数的地址,为了方便hook,我们也可以在编译的时候直接导出符号表,这样知道函数名也能hook
用python写一个hook的脚本
import frida
import sys
session = frida.attach("target")
script = session.create_script("""
Interceptor.replace(ptr("%s"), new NativeCallback(function(input) {
var password = input.readCString();
console.log("[*] Intercepted password: " + password);
// 不管输入什么,都返回 1 (成功)
return 1;
}, 'int', ['pointer']));
""" % int(sys.argv[1], 16))
script.load()
sys.stdin.read()脚本的流程大概是:先attach target进程并将frida的动态库注入到目标进程中,session.create_script就是创建一个js脚本并在目标进程的地址空间内执行;js脚本就是直接将对应的目标函数进行替换,Interceptor.replace(目标地址, 新函数),new NativeCallback的后两个参数,int表示返回类型,['pointer']表示参数列表
效果如下,先启动target程序

然后获取地址启动hook脚本
python hook.py 0x55c03e7c7229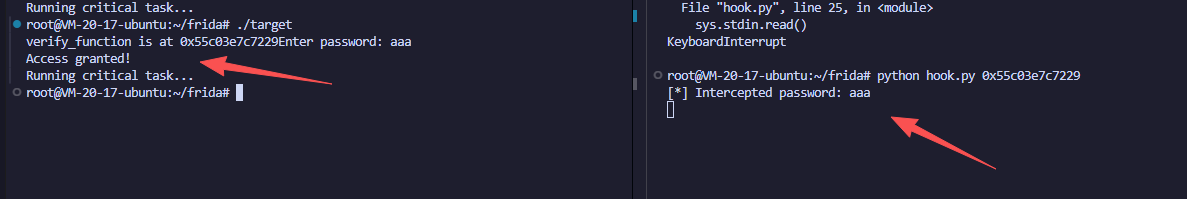
可以看到随便输入任何数字,此时已经成功绕过了
安卓hook
SSL Pinning绕过
python客户端模拟
这里也是使用python来作为一个模拟,主要是先学习一下
SSL Pinning就是SSL证书绑定机制,通常见于手机app,App 在代码中硬编码服务器证书的“指纹”(比如 SHA256 哈希),例如:
// Android 示例(OkHttp)
CertificatePinner certificatePinner = new CertificatePinner.Builder()
.add("api.bank.com", "sha256/AAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAA=")
.build();
OkHttpClient client = new OkHttpClient.Builder()
.certificatePinner(certificatePinner)
.build();所以有时候即使在手机上安装了burp的证书,app计算证书发现和编码的指纹不一致时,就会导致抓包失败
首先创建一个带SSL Pining的客户端
import ssl
import socket
import hashlib
import sys
# 模拟目标服务器的证书指纹(比如 google.com 的真实指纹)
EXPECTED_PIN = "7d34e8d0c1b9f8a7e6c5d4b3a2f1e0d9c8b7a6f5e4d3c2b1a0f9e8d7c6b5a4f3"
def verify_pin(cert_der):
"""模拟证书绑定:校验证书 DER 的 SHA256"""
actual_pin = hashlib.sha256(cert_der).hexdigest()
print(f"[Client] Got cert pin: {actual_pin}")
return actual_pin == EXPECTED_PIN
def connect_with_pinning(host, port=443):
# 创建 socket
sock = socket.create_connection((host, port))
# 创建 SSL 上下文
ctx = ssl.create_default_context()
# 获取原始证书(用于 pinning)
with ctx.wrap_socket(sock, server_hostname=host) as ssock:
cert_der = ssock.getpeercert(binary_form=True)
if not verify_pin(cert_der):
print("[!] SSL Pinning failed! Connection aborted.")
return None
print("[+] SSL Pinning passed. Sending request...")
ssock.send(b"GET / HTTP/1.1\r\nHost: " + host.encode() + b"\r\n\r\n")
return ssock.recv(1024)
if __name__ == "__main__":
if len(sys.argv) < 2:
print("Usage: python3 pinned_client.py <host>")
sys.exit(1)
host = sys.argv[1]
try:
response = connect_with_pinning(host)
if response:
print("[*] Response:", response[:200].decode(errors='ignore'))
except Exception as e:
print("[!] Error:", e)这个脚本会:
-
连接指定 HTTPS 站点
-
获取服务器证书的 DER 编码
-
计算其 SHA256 并与
EXPECTED_PIN比较 -
不匹配就拒绝通信
比如我们这里去连接一下百度
python3 pinned_client.py www.baidu.com
这里我们硬编码了一个假的 EXPECTED_PIN,所以总是失败,接下来尝试用Frida去绕过一下SSL Pinning
思路其实和前面基础使用的绕过密码验证一样:
-
hook python的verify_pin函数
-
强制函数返回True
但注意:Frida 默认不能直接 hook Python 函数(因为 Python 是解释型语言,函数不在 native 层)。
所以我们需要hook底层的c函数:
Python 的 hashlib.sha256() 最终调用的是 OpenSSL 的 SHA256_Update 或 libc 的哈希函数。
让ai给我写了好多版去hook openssl底层函数,但是失败了,放一个失败的代码在这,有机会再改吧,目前对frida还不是很熟悉
// bypass_pinned.js —— 终极修复版:适配 Ubuntu 20.04 + 静态链接 Python
'use strict';
(function () {
let hooked = false;
let pyApiReady = false;
// 全局函数指针
let _PyGILState_Ensure, _PyGILState_Release, _PyRun_SimpleString;
function initPythonAPI() {
if (pyApiReady) return true;
// 方法 1: 尝试从主程序路径查找(最可靠)
const mainModule = Process.enumerateModules()[0]; // 主程序通常是第一个
console.log("[*] Main module candidate:", mainModule.name);
// 或者遍历所有模块找 python3
let pythonModule = null;
const modules = Process.enumerateModules();
for (let i = 0; i < modules.length; i++) {
const name = modules[i].name;
if (name.includes("python3") && !name.includes("lib")) {
pythonModule = modules[i];
break;
}
}
if (!pythonModule) {
console.warn("[-] Python main module not found in module list");
return false;
}
const PyRun_SimpleString = Module.findExportByName(pythonModule.name, "PyRun_SimpleString");
const PyGILState_Ensure = Module.findExportByName(pythonModule.name, "PyGILState_Ensure");
const PyGILState_Release = Module.findExportByName(pythonModule.name, "PyGILState_Release");
if (!PyRun_SimpleString || !PyGILState_Ensure || !PyGILState_Release) {
console.warn("[-] Required Python symbols not found in", pythonModule.name);
return false;
}
_PyGILState_Ensure = new NativeFunction(PyGILState_Ensure, 'pointer', []);
_PyGILState_Release = new NativeFunction(PyGILState_Release, 'void', ['pointer']);
_PyRun_SimpleString = new NativeFunction(PyRun_SimpleString, 'int', ['pointer']);
pyApiReady = true;
console.log("[*] Python C API initialized from:", pythonModule.name);
return true;
}
function injectPythonCode(code) {
if (!pyApiReady) {
console.warn("[-] Python API not ready, skipping injection");
return;
}
const gstate = _PyGILState_Ensure();
try {
_PyRun_SimpleString(Memory.allocUtf8String(code));
} finally {
_PyGILState_Release(gstate);
}
}
function tryHookLibcrypto() {
if (hooked) return;
const libcrypto = Process.findModuleByName("libcrypto.so.1.1");
if (!libcrypto) {
setTimeout(tryHookLibcrypto, 500);
return;
}
const SHA256_Final = Module.findExportByName(libcrypto.name, "SHA256_Final");
if (!SHA256_Final) {
console.error("[-] SHA256_Final not found!");
return;
}
Interceptor.attach(SHA256_Final, {
onEnter(args) {
this.md = args[0];
},
onLeave() {
try {
const hashBytes = this.md.readByteArray(32);
const hashHex = [...new Uint8Array(hashBytes)]
.map(b => b.toString(16).padStart(2, '0'))
.join('');
console.log("[+] Real cert SHA256:", hashHex);
// 确保 Python API 已初始化
if (initPythonAPI()) {
injectPythonCode(`
import sys
if 'pinned_client' in sys.modules:
import pinned_client
pinned_client.EXPECTED_PIN = "${hashHex}"
print("[*] EXPECTED_PIN updated to match real cert!")
`);
}
} catch (e) {
console.log("[-] Hash processing error:", e);
}
}
});
hooked = true;
console.log("[*] Successfully hooked libcrypto.so.1.1");
}
// 启动:延迟 1 秒确保所有模块加载完毕
setTimeout(() => {
console.log("[*] Starting hook initialization...");
tryHookLibcrypto();
}, 1000);
})();然后启动的命令如下:
frida -l bypass_pinned.js -q -- /usr/bin/python3 pinned_client.py www.baidu.com结果如下:

估计是修改EXPECTED_PIN失败了
然后又试了一些其他的方式,比如:Hook PyEval_EvalFrameDefault(CPython 虚拟机中执行 Python 字节码的核心函数)、修改python字节码等方式,均未成功,所以暂时留个坑吧,毕竟遇到需要hook python函数的场景还是比较少的。
c语言客户端模拟
这边改成c语言客户端来进行模拟,平时遇到这种的场景应该会更多一些
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <openssl/sha.h>
#include <openssl/ssl.h>
#include <openssl/err.h>
// 假的预期指纹(故意设错)
const char* EXPECTED_PIN = "7d34e8d0c1b9f8a7e6c5d4b3a2f1e0d9c8b7a6f5e4d3c2b1a0f9e8d7c6b5a4f3";
int verify_certificate_pin(const unsigned char* der_data, int der_len) {
unsigned char hash[SHA256_DIGEST_LENGTH];
char pin[65]; // 64 hex + null
SHA256(der_data, der_len, hash);
for (int i = 0; i < SHA256_DIGEST_LENGTH; i++) {
sprintf(&pin[i*2], "%02x", hash[i]);
}
printf("[Client] Got cert pin: %s\n", pin);
int result = (strcmp(pin, EXPECTED_PIN) == 0);
printf("[Client] Pin check result: %d\n", result);
return result;
}
// 为简化,我们不真正联网,只模拟校验逻辑
int main() {
// 模拟一段证书 DER 数据(随便给)
unsigned char fake_cert[] = "fake-cert-data-for-demo";
if (verify_certificate_pin(fake_cert, sizeof(fake_cert)-1)) {
printf("[+] SSL Pinning bypassed!\n");
} else {
printf("[-] SSL Pinning blocked.\n");
}
return 0;
}然后进行编译
# 如果没有openssl开发库需要安装
sudo apt install libssl-dev
gcc -rdynamic -o ssl_pinning ssl_pinning.c -lssl -lcryptobypass的frida脚本
/*
* bypass_ssl.js - 修正版
*
* 核心思路:
* 1. Process.getModuleByName 获取主程序模块。
* 2. module.enumerateSymbols() 遍历该模块的所有符号。
* 3. 通过字符串匹配 (sym.name.includes(...)) 找到目标函数。
* 4. Interceptor.replace() 使用找到的地址进行 Hook。
*/
console.log("[*] Script loaded. Searching for 'ssl_pinning' module...");
// 1. 获取目标进程的主模块
const module = Process.getModuleByName("ssl_pinning");
if (module) {
console.log(`[+] Found module: ${module.name} at base: ${module.base}`);
let verifyFuncAddr = null;
// 2. 遍历模块的所有符号
const symbols = module.enumerateSymbols();
for (const sym of symbols) {
// 3. 查找包含我们目标函数名的符号
if (sym.name.includes("verify_certificate_pin")) {
verifyFuncAddr = sym.address;
console.log(`[+] Found 'verify_certificate_pin' symbol at: ${verifyFuncAddr}`);
console.log(` - Symbol details: ${JSON.stringify(sym)}`);
break; // 找到后就跳出循环
}
}
if (verifyFuncAddr) {
// 4. 使用找到的函数地址进行 Hook
Interceptor.replace(verifyFuncAddr, new NativeCallback(() => {
console.log("[***] SSL Pinning Bypassed! Always returning TRUE. [***]");
return 1; // 始终返回 1 (true)
}, 'int', ['pointer', 'int']));
console.log("[+] Hook installed on 'verify_certificate_pin'.");
} else {
console.log("[-] Could not find the 'verify_certificate_pin' symbol in the module.");
}
} else {
console.log("[-] Module 'ssl_pinning' not found. Is the process name correct?");
}
这脚本还是让Gemini2.5Pro写出来的,其他模型咋改都是错的
运行命令
frida -l bypass_ssl.js -q ./ssl_pinning效果如下:
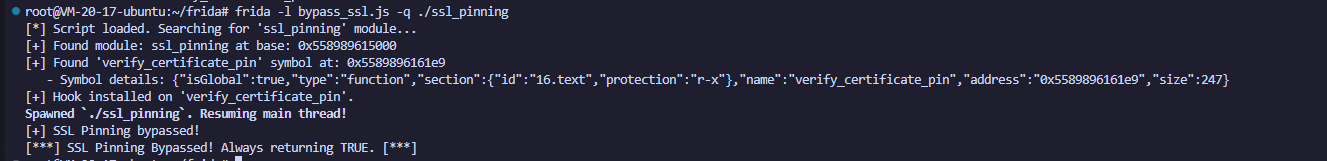
这样就成功了,脚本的原理通过代码里的注释也能够很好地看懂流程
问题(待解决)
之前的ai普遍给的做法都是使用类似下面的脚本来进行hook
console.log("[*] Script loaded. Using findExportByName(null, ...)");
// 因为你用了 -rdynamic, 所以函数在动态符号表里
// 我们用 null 来搜索所有模块
const verifyFunc = Module.findExportByName(null, "verify_certificate_pin");
if (verifyFunc) {
console.log(`[+] Found exported function 'verify_certificate_pin' at: ${verifyFunc}`);
Interceptor.replace(verifyFunc, new NativeCallback(() => {
console.log("[***] SSL Pinning Bypassed via findExportByName! Always returning TRUE. [***]");
return 1;
}, 'int', ['pointer', 'int']));
console.log("[+] Hook installed on 'verify_certificate_pin'.");
} else {
console.log("[-] Could not find 'verify_certificate_pin' as an exported function.");
console.log("[-] This shouldn't happen if you compiled with -rdynamic.");
}
然后无一例外都会报类似下面的错误
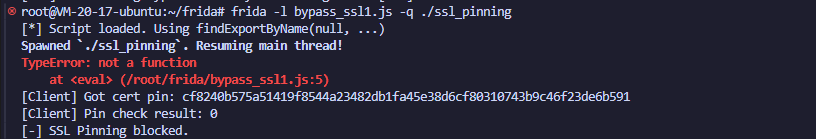
也就是用Module.findExportByName来找verify_certificate_pin这个函数,结果确找不到;这里null的意思就是可以去遍历所有模块来找有没有导出的verify_certificate_pin函数,也可以指定模块名,有关模块名的理解看下面的列模块名的脚本就可以知道了
但是我前面的编译命令-rdynamic就代表指示链接器将程序的所有符号导出到动态符号表当中(.dynsym),findExportByName就是从动态符号表里面去找对应的函数的
在ELF中还有另一种符号表.symtab,它包含所有的符号信息:全局函数、静态函数、文件名、变量等。它主要用于调试(比如用 gdb )和链接。默认情况下,编译后的二进制文件会包含这个表,但可以通过 strip 命令移除它以减小文件大小。
gcc -rdynamic 这个标志的作用,就是告诉链接器:“请把.symtab里的所有全局符号都复制一份,也放到.dynsym里去。
emmm,所以这里我也不知道为什么会找不到,我们可以用下面的脚本看一下所有的模块名
// list_modules.js
// 这个脚本会打印出目标进程加载的所有模块
console.log("[*] Script loaded. Enumerating all modules...");
// 获取所有已加载模块的列表
const modules = Process.enumerateModules();
// 遍历列表并打印每个模块的详细信息
modules.forEach(function(module) {
// 使用 JSON.stringify 可以方便地查看所有属性
console.log(JSON.stringify(module));
});
console.log("\n[*] Enumeration complete.");
console.log(`[*] Total modules found: ${modules.length}`);
// 你可以特别关注主程序模块
const mainModule = Process.findModuleByName("ssl_pinning");
if (mainModule) {
console.log("\n--- Highlight: Found main module by name 'ssl_pinning' ---");
console.log(JSON.stringify(mainModule));
console.log("---------------------------------------------------------");
}结果如下:
root@VM-20-17-ubuntu:~/frida# frida -l list_modules.js -q ./ssl_pinning
[*] Script loaded. Enumerating all modules...
{"name":"ssl_pinning","version":null,"base":"0x55c3e0d44000","size":16416,"path":"/root/frida/ssl_pinning"}
{"name":"linux-vdso.so.1","version":null,"base":"0x7fff6a7f4000","size":2866,"path":"linux-vdso.so.1"}
{"name":"libcrypto.so.1.1","version":null,"base":"0x7f9e1c5c0000","size":2977696,"path":"/usr/lib/x86_64-linux-gnu/libcrypto.so.1.1"}
{"name":"libc-2.31.so","version":null,"base":"0x7f9e1c3ce000","size":2037344,"path":"/usr/lib/x86_64-linux-gnu/libc-2.31.so"}
{"name":"libdl-2.31.so","version":null,"base":"0x7f9e1c3c8000","size":20752,"path":"/usr/lib/x86_64-linux-gnu/libdl-2.31.so"}
{"name":"libpthread-2.31.so","version":null,"base":"0x7f9e1c3a5000","size":140408,"path":"/usr/lib/x86_64-linux-gnu/libpthread-2.31.so"}
{"name":"ld-2.31.so","version":null,"base":"0x7f9e1c8b4000","size":192912,"path":"/usr/lib/x86_64-linux-gnu/ld-2.31.so"}
{"name":"librt-2.31.so","version":null,"base":"0x7f9e1a39c000","size":39904,"path":"/usr/lib/x86_64-linux-gnu/librt-2.31.so"}
{"name":"libm-2.31.so","version":null,"base":"0x7f9e1a24d000","size":1368336,"path":"/usr/lib/x86_64-linux-gnu/libm-2.31.so"}
[*] Enumeration complete.
[*] Total modules found: 9
--- Highlight: Found main module by name 'ssl_pinning' ---
{"name":"ssl_pinning","version":null,"base":"0x55c3e0d44000","size":16416,"path":"/root/frida/ssl_pinning"}
---------------------------------------------------------
Spawned `./ssl_pinning`. Resuming main thread!
[Client] Got cert pin: cf8240b575a51419f8544a23482db1fa45e38d6cf80310743b9c46f23de6b591
[Client] Pin check result: 0
[-] SSL Pinning blocked.可以看到确实是有ssl_pinning这个主模块名的
所以这里是一个待解决的问题,等查查资料再来补充🤔
参考
https://cloud.tencent.com/developer/article/2192343
https://frida.re/docs

